

06/06/01
To convert some carbureted vehicles to EFI, we recommend fitting a fuel surge tank to avoid fuel feed problems, especially during hard cornering. This is also useful on many stock EFI cars which have poorly baffled tanks. The surge tank stores a small amount of fuel for the high pressure pump to pick up if flow from the main tank is interrupted for any reason.
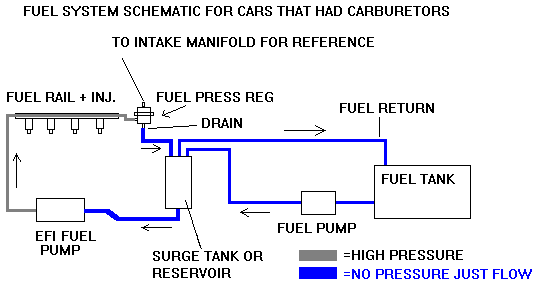
Usually the tank is mounted in the engine compartment. Fuel is piped to it by either a stock engine driven mechanical pump or a low pressure electric pump. Often the stock electric pump can be used. A high pressure EFI pump will be mounted below the surge tank. The fuel gravity feeds into this pump and goes to the fuel rail. Fuel not used by the engine is returned from the rail, through the fuel pressure regulator, to the top of the surge tank. From here, if the surge tank is full, fuel is returned back to the main fuel tank. The schematic below shows a common setup:

Most tanks will have three fittings on the top, one for feed from the low pressure pump, one for fuel returned through the fuel pressure regulator and one for the return back to the main fuel tank. Usually only one fitting is used on the bottom of the tank for feeding the high pressure pump.
Tanks are usually about .5 to 1 liter in capacity, made from either steel or aluminum tubing. The tubing is usually 2.5 or 3 inch diameter and .050 to .075 wall thickness. A long tank allows any trapped air to rise to the top so it does not enter the high pressure pump. Threaded bosses are welded to the top and bottom caps or sides as in the example below. Usually 1/8 NPT or 1/4 NPT fittings are used but AN type fittings can also be used depending on your plumbing preferences.


This tank has 3 lower fittings for twin pumps plus a drain fitting. Earls NPT weld-in bosses are used. This tank is made from 3 inch, 6061 T6 tubing. Mild steel exhaust tubing also works well. All joints are carefully TIG welded. Test for leaks before installing.